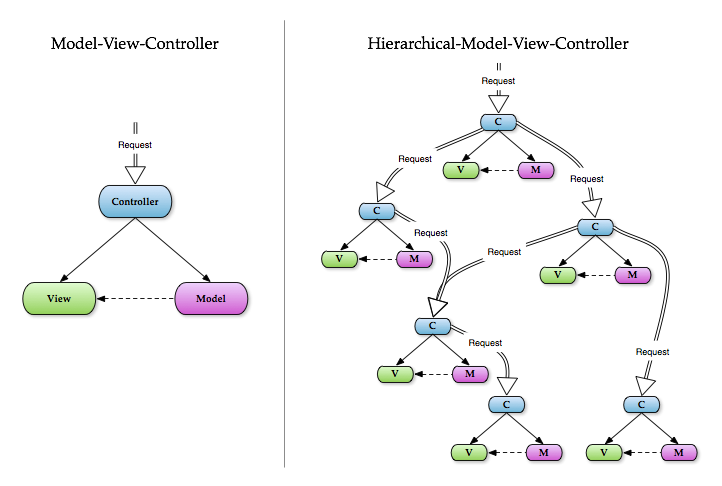
Is the “widgetization” architecture according to the Wikipedia. Basically, each module has (models, views and controllers). Each module provides functionalities. The modules talk to each other to provide functionalities as a System. The question is : How they talk to each other? This seems to not be important, but impacts when we talk about system maintenance and bug fixing.Lets imagine an application that contains the modules : Human Resources, Sales and Security (for entrance control).All the people that work in our organisation have a record in the system, done via the Human Resources module. How the Security module gets that information? Of course the Human resources module has a model named Person. Two things can Happen.
- The Security module can have another model with the same name that points to the same table if SQL Database or collection if no SQL.
- The security module can retrieve the information from the Human Resources Module Model, directly.
What are the impacts of both choices ?
THE FIRST ALTERNATIVE
The problem here is that this module is violating the business logic. Each module should know only about itself and about another modules Interfaces (functionalities the provide) and not about their internal processes to emulate them.
THE SECOND ALTERNATIVE
The Human Resources module can change the way it handles the stuff, can even stop Having that model, rename it or change its function names. If There are two developers working each on a different module, this will probably happen.A model was never meant to be the Communication vehicle between modules, but it has never been told what/who is responsible for such communication. Thats the HMVC Limitation. If you look at the figure below you will see that the module A makes calls to the module B resources. Thats wrong. The module A should never know what is inside de Module B, OR how it works. What matters is what the module provides to others. The module interface. This communication feature is provided in the Strict HMVC.
SHMVC
It might be the HMVC Evolution. The only difference is that it provides a way of communication among modules. Each module defines an interface to serve another modules. This will make the system easy to maintain. The secret is : define an interface that is never going to change. The module can change the way it implements, but cant stop implementing. There is no more direct modules resources access.Resources are private but the interface is public.












Comentários Recentes